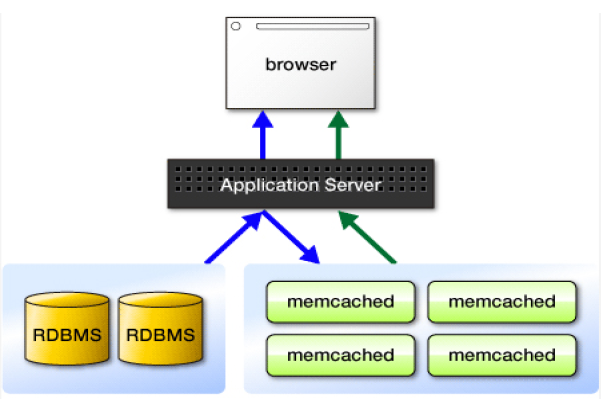
Memcached
is an in-memory key-value store for small chunks of arbitrary data
(strings, objects) from results of database calls, API calls, or page
rendering.
Memcached is a general-purpose distributed memory caching system that was originally developed by Danga Interactive for LiveJournal,
but is now used by many other sites. It is often used to speed up
dynamic database-driven websites by caching data and objects in RAM to
reduce the number of times an external data source (such as a database
or API) must be read. Memcached runs on Unix, Linux, Windows and Mac OS X
and is distributed under a permissive free software license.
Memcached's
APIs provide a giant hash table distributed across multiple machines.
When the table is full, subsequent inserts cause older data to be purged
in least recently used (LRU) order.
Architecture
Who uses Memcache?
- YouTube
- Reddit
- Zynga
- Facebook
- Orange
- Twitter
- Wikipedia
- Google App Engine, AppScale, Windows Azure and Amazon Web Services also offer a memcached service through an API
Used For?
Pros
1) Reduces database load.
2) Perfect for websites with high database load.
3) Significantly reduces the number of retrieval requests to database
4) Cuts down the I/O access (hard disk)
Cons
1) Not a persistent data store.
2) Not a database.
3) Not application specific
4) Cannot cache large object
Configuring Memcached (For Ubuntu)
Step 1) Install Libevent
$ cd libevent-1.4.11-stable$ autoconf
$ ./configure --prefix=/usr/local
$ make
$ sudo make install
$ ./configure --prefix=/usr/local
$ make
$ sudo make install
Step 2) Install Memcached
$ cd memcached-1.4.0$ autoconf$ ./configure --prefix=/usr/local$ make$ sudo make install
Step 3) Run memcached
Start memcached as a daemon with 512MB of memory on port 11211(default).
Then you can telnet to the server and port and use any of the available commands.
$ memcached -d -m 512 127.0.0.1 -p 11211
$ telnet localhost 11211Trying ::1...
Connected to localhost.
Escape character is '^]'.get joe
ENDset joe 0 3600 10 (Note: TTL 3600 and 10 bytes)California
STOREDget joe
VALUE joe 0 10
California
END
$ telnet localhost 11211Trying ::1...
Connected to localhost.
Escape character is '^]'.get joe
ENDset joe 0 3600 10 (Note: TTL 3600 and 10 bytes)California
STOREDget joe
VALUE joe 0 10
California
END
Step 4) Spy Memcached (Memcached Java Client)
public class Users implements Serializable{
private int id;
private String name ;
// Getter and Setter methods
}
public class MemcachedDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Users users = new Users();
users.setId(1);
users.setName("Sunil123");
try {
MemcachedClient c=new MemcachedClient(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 1121));
c.set("someKey_1", 2592000, users);
Object myObject=c.get("someKey_1");
System.out.println("Object 1: " + myObject);
System.out.println("Statistics: " + c.getStats());
System.out.println("Statistics of individual Items: " + c.getStats("items"));
c.delete("someKey_2");
c.shutdown();
c=null ;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}